3.1 Measures to prevent pest infestations
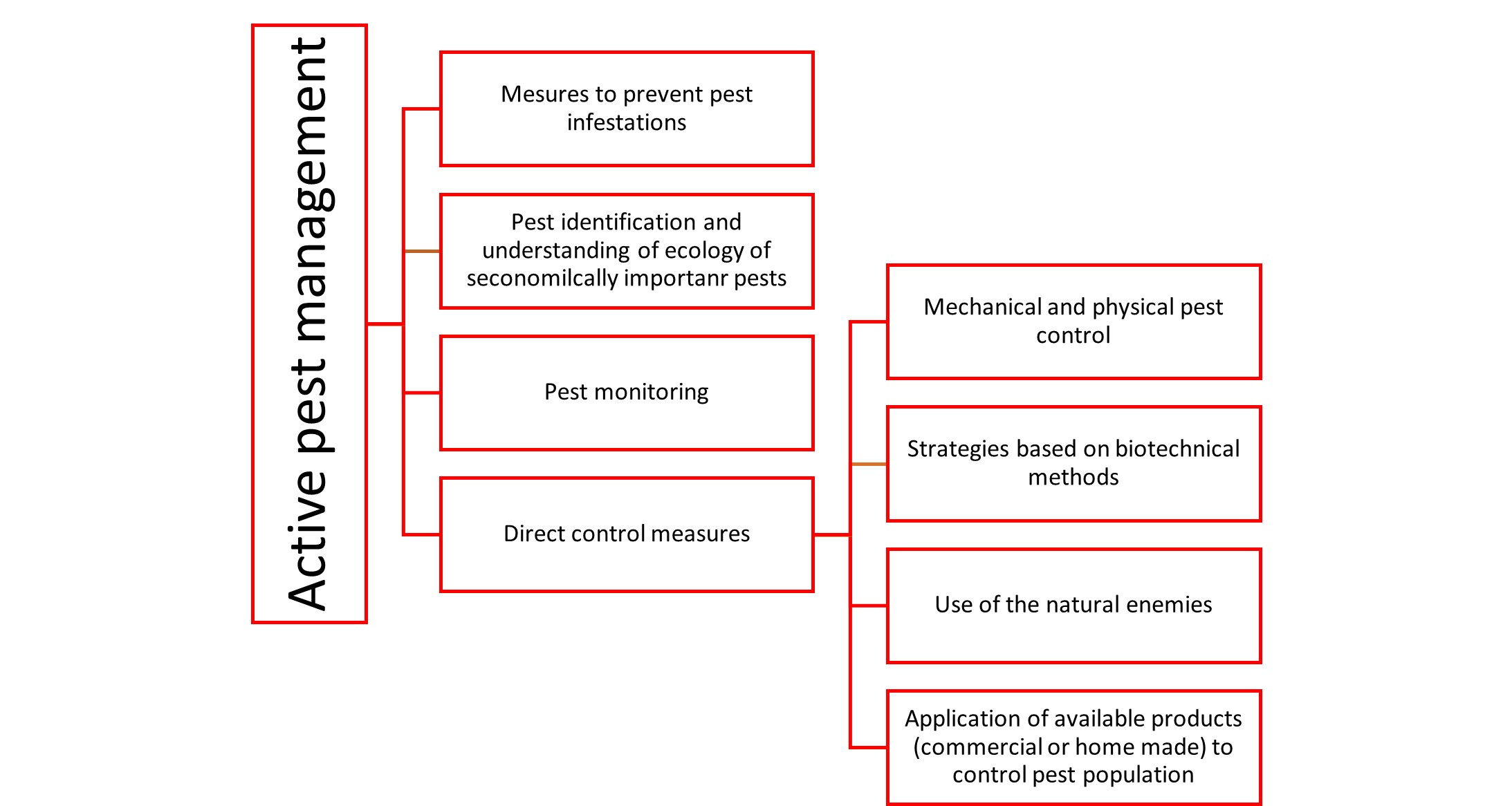
METHODS AND TOOLS TO MANAGE PESTS
Managing pest populations is extremely important in any crop production. Pests can cause different types of damage, which we basically divide into direct and indirect damage.
Direct damage includes:
- yield loss, which occurs because the plants have died completely (in the case of seed damage at germination or root), because their leaf mass is damaged (due to the pests feeding on the leaves) or because they have lost their vitality (which occurs due to the pests feeding on the plants by sucking on them), making assimilation more difficult; all of which result in lower yields.
- (b) Reduction in product quality, which includes qualitative changes in the composition of plant products (e.g. aphid infestation on carrots leads to poor taste of carrots)
Indirect damage includes:
- Transmission of plant pathogens - in some cases pest damage opens the way for pathogen infection, and in some cases (aphid) pests actively transmit pathogens (viruses).
- Decreased market value of the product due to contamination by pests or their secretions (in the case of caterpillars, the presence of caterpillars and / or their droppings, the presence of honeydew when infesting aphids, moths, etc.)
- Reduced assimilation due to the appearance of smut fungi covering the leaves and fruit on which honeydew has remained
To prevent the damage described above and to avoid creating conditions for uncontrolled growth of pest populations, which may lead to increased damage in future years, pests must be actively controlled. The basic components of active pest control are shown in Figure 3.1.